The journey through menopause is unique for every woman, yet it’s a natural transition we all share. Whether you’re approaching this phase of life or seeking to understand what lies ahead, this comprehensive guide will help you navigate the changes with confidence and knowledge.
Overview
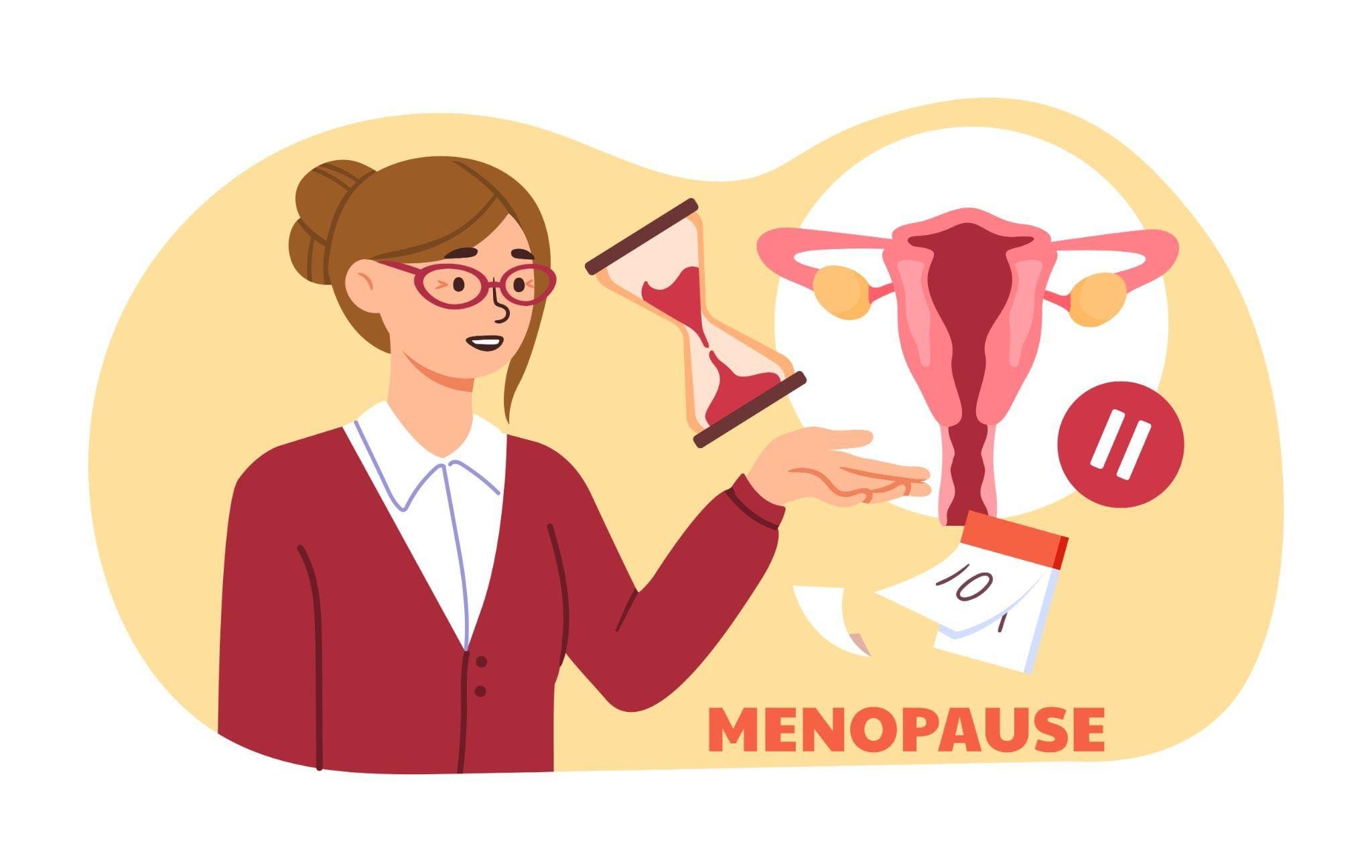
What is Menopause and When Does It Begin?
Menopause marks a significant milestone in a woman’s life, officially occurring when you’ve gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. While the average age is 52, the journey typically begins in your mid-40s with a phase called perimenopause or menopause transition.
During this time, your ovaries gradually reduce their production of essential reproductive hormones, particularly estrogen and progesterone. This natural decline triggers various physical and emotional changes that can span several years.
Understanding the Three Stages of the Menopausal Journey
1. The Transition Phase: Perimenopause
Perimenopause often starts 8-10 years before menopause itself. During this time, you might experience: – Irregular periods that vary in flow and frequency – Initial symptoms like hot flashes and night sweats – Mood fluctuations and premenstrual syndrome changes – Changes in your sex drive
2. The Milestone: Menopause
Once you’ve gone a full year without periods, you’ve officially reached menopause. This represents a permanent shift in your reproductive system, as your ovaries have stopped releasing eggs and significantly reduced hormone production.
3. The New Normal: Postmenopause
This phase encompasses all the years following menopause, bringing both challenges and opportunities for renewed well-being. During this time, most women experience a gradual easing of symptoms, though some may persist.
Common Symptoms and Their Impact
Every woman’s experience with menopause is different, but some common symptoms include:
Physical Changes:
- Hot flashes and night sweats
- Vaginal dryness and discomfort during sex
- Hair loss or thinning
- Insomnia and sleep disruptions
- Headaches and physical discomfort
Emotional Changes:
- Mood swings
- Depression and anxiety
- Changes in cognitive function
- Fluctuating energy levels
Understanding Early and Premature Menopause
While natural menopause typically occurs between 45-55 years, some women experience it earlier. Premature menopause can occur before age 40, sometimes due to: – Primary ovarian insufficiency – Medical treatments like radiation therapy – Surgical removal of your ovaries
Diagnosis and Testing
Healthcare providers typically diagnose menopause based on your symptoms and menstrual Cycle history. However, they might recommend: – Blood tests to check hormone levels – Discussions about your symptoms and their impact – Regular health screenings
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
1. Hormone-Based Treatments
Hormone therapy remains one of the most effective treatments for menopausal symptoms. Options include: – Traditional hormone replacement therapy – Low-dose birth control pills for perimenopausal symptoms – Local hormone treatments for specific symptoms
2. Non-hormonal Treatments
For women who can’t or prefer not to use hormone therapy, alternatives include: – Antidepressants for mood symptoms and hot flashes – Gabapentin for sleep issues and hot flashes – Natural supplements (discuss with your healthcare provider)
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Simple changes can make a significant difference: – Maintaining regular exercise – Reducing caffeine intake – Quitting smoking – Practicing stress-reduction techniques
Health Considerations During and After Menopause
The hormonal changes of menopause can affect various aspects of your health:
Bone Health:
- Increased risk of osteoporosis and fracture
- Importance of bone densitometry screening
- Calcium and vitamin D supplementation
Heart Health:
- Higher risk of cardiovascular disease
- Need to monitor blood pressure and high cholesterol
- Importance of regular exercise
Weight Management:
- Hormone changes can impact your weight
- Importance of balanced nutrition
- Role of regular physical activity
Sexual Health and Intimacy
Changes in sexual health are common during menopause: – Managing vaginal dryness – Addressing changes in sex drive – Maintaining intimate relationships – Using appropriate lubricants and moisturizers
Supporting Your Overall Well-being
Managing menopause successfully involves a holistic approach: – Regular medical check-ups – Mental health support when needed – Building a support network – Staying informed about your health
The Impact of Low Hormones
Understanding how low estrogen and low testosterone affect your body can help you better manage symptoms: – Changes in skin and hair – Effects on bone density – Impact on mood and energy – Influence on sexual function
Managing Specific Menopause Symptoms
Understanding Hot Flashes and Night Sweats
These vasomotor symptoms affect up to 75% of menopausal women: – What triggers them – Common patterns and duration – Management strategies: – Layered clothing – Keeping room temperature cool – Avoiding trigger foods – Relaxation techniques – When to consider medical intervention.
Sleep Challenges and Insomnia
Sleep disruption during menopause can significantly impact quality of life: – Understanding the connection between hormones and sleep – Common sleep disturbances – Creating a sleep-friendly environment – Natural remedies and sleep hygiene – Medical treatments when needed.
Mood Changes and Mental Health
The emotional impact of menopause shouldn’t be underestimated: – Recognizing signs of depression – Anxiety and mood swings – Impact on relationships – Support strategies: – Counseling options – Support groups – Lifestyle modifications – Medical interventions when necessary.
Understanding Reproductive Health Risks
The uterus and reproductive system undergo significant changes during menopause. These changes can affect your health in various ways:
Uterine Health:
- Changes to the uterus during menopause
- Importance of regular check-ups
- Signs that require medical attention
- Treatment options for uterine issues
Breast Cancer Awareness:
- Increased risk factors during menopause
- Regular screening importance
- Connection between hormone therapy and breast cancer risk
- Preventive measures and early detection
- Working with healthcare providers for monitoring
When to Seek Medical Help
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience: – Unusual vaginal bleeding – Severe mood changes – Debilitating symptoms – Concerns about your transition.
Looking Ahead: Life After Menopause
While menopause marks the end of reproductive years, it opens a new chapter in life: – Focus on overall health and wellness – Opportunity for personal growth – Time to prioritize self-care
Conclusion
Menopause is a natural transition that every woman experiences differently. Understanding your body’s changes, knowing your treatment options, and maintaining open communication with your healthcare provider can help you navigate this phase of life with confidence. Remember, there’s no “right” way to experience menopause – your journey is unique to you.
Resources and Support
Finding reliable information and support is crucial during your menopause journey. Consider: – Joining local support groups – Consulting with menopause specialists – Exploring online communities – Reading trusted medical resources – Connecting with other women going through similar experiences
Remember to always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs and circumstances
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Menopause
Menopause typically occurs between ages 45-55, with an average age of 52. However, perimenopause can start as early as the mid-40s, and some women experience premature menopause before 40.
Early signs include irregular periods, hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, vaginal dryness, and sleep disturbances. Some women may also experience weight changes and decreased energy levels.
Yes, hormonal changes can contribute to mood swings, anxiety, depression, and difficulty concentrating. Seeking medical advice, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and considering therapy or support groups can help manage emotional well-being.
Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management, and avoiding triggers like caffeine and alcohol can help. Herbal supplements may also offer relief, but consult your doctor before use.
HRT can effectively relieve symptoms like hot flashes and bone loss, but it’s not suitable for everyone. Discuss the benefits and risks with your doctor to determine the best option for your health needs.










 No need to worry, your data is 100% Safe with us!
No need to worry, your data is 100% Safe with us!
1 thought on “Menopause is a natural transition every woman goes through.”
Pingback: Menopause Myths Busted What Every Woman Should Know