Menopause is a natural milestone in a woman’s life, marking the end of her reproductive years. While it’s a universal experience, every woman’s journey through menopause is unique. Let’s explore the signs of menopause, its causes, and how to manage its effects effectively.
What is Menopause?
Menopause signifies the end of menstruation and typically occurs around the age of 51. It is diagnosed after a woman has gone 12 consecutive months without a menstrual period. During this phase, the ovaries reduce the production of estrogen and other reproductive hormones, leading to the cessation of the menstrual cycle.
In some cases, menopause is induced earlier due to medical interventions like surgery or chemotherapy. Whether natural or induced, menopause is accompanied by hormonal changes that affect the body and mind.
Stages of Menopause
Menopause is a gradual process that unfolds in three key stages:
1. Perimenopause
This transitional phase begins several years before menopause. Estrogen levels fluctuate, causing irregular periods, mood swings, and hot flashes. Perimenopause typically starts in a woman’s 40s but can begin earlier.
2. Menopause
Menopause officially starts when a woman has gone 12 months without a menstrual period. At this stage, the ovaries cease releasing eggs, and estrogen production significantly decreases.
3. Postmenopause
This phase follows menopause and lasts for the remainder of a woman’s life. While some symptoms may ease, the body’s low estrogen levels increase the risk of health issues such as osteoporosis and cardiovascular disease.
Common Symptoms of Menopause
Menopause symptoms can vary, but some of the most common include:
-
- Irregular periods: Changes in the menstrual cycle are often one of the first signs.
-
- Hot flashes: Sudden feelings of warmth, often accompanied by sweating.
-
- Night sweats: Hot flashes that occur during sleep.
-
- Vaginal dryness: Reduced lubrication, leading to discomfort.
-
- Mood changes: Anxiety, irritability, and depression.
-
- Sleep disturbances: Insomnia or difficulty staying asleep.
-
- Weight gain: Changes in metabolism can lead to increased body weight.
-
- Decreased libido: A common symptom due to hormonal shifts.
These changes result from the body adapting to fluctuating hormone levels.
What Signals the End of Menopause?
The end of menopause is marked by a full year without a menstrual period. By this point, the body’s estrogen levels stabilize at a lower level. While some symptoms, like hot flashes, may persist, others, such as irregular periods, no longer occur.
Causes of Menopause
The primary cause of menopause is natural aging. However, other factors can accelerate the process:
-
- Surgical menopause: Removal of the ovaries triggers an immediate onset.
-
- Medical treatments: Chemotherapy or radiation therapy can damage the ovaries.
-
- Premature menopause: Occurs before age 40 due to genetics or autoimmune conditions.
Hormonal Imbalance Symptoms
During menopause, hormonal changes can lead to various physical and emotional symptoms, including:
-
- Fatigue and energy loss.
-
- Hair thinning or hair loss.
-
- Difficulty concentrating.
-
- Breast tenderness.
If these symptoms are severe, consult a healthcare professional for advice on management options.
How to Manage Menopause Symptoms
Managing menopause effectively requires a combination of treatments and lifestyle changes:
1. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
HRT helps alleviate symptoms by replacing declining levels of estrogen and progesterone.
2. Healthy Lifestyle Choices
-
- Follow a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
-
- Engage in regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight and improve mood.
-
- Practice stress-relief techniques like yoga and meditation.
3. Non-Hormonal Options
Medications like antidepressants or supplements may help with mood swings and sleep disturbances. Natural remedies, such as soy isoflavones, can also provide relief.
Can You Influence Your Menstrual Cycle During Perimenopause?
While regulating the menstrual cycle during perimenopause isn’t always possible, certain measures may help:
-
- Consult your doctor about hormonal therapies.
-
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
-
- Incorporate phytoestrogen-rich foods, like flaxseeds and soy, into your diet.
Health Risks After Menopause
Low estrogen levels after menopause increase the risk of:
-
- Osteoporosis: Reduced bone density leads to a higher likelihood of fractures.
-
- Heart disease: Estrogen’s protective effect on the heart diminishes, raising the risk of cardiovascular issues.
-
- Weight gain: Changes in metabolism can lead to increased body fat.
Preventive measures, such as regular health screenings and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, are crucial.
Conclusion
Menopause is a significant life event that can bring both challenges and opportunities for growth. Understanding the symptoms of menopause and knowing how to manage them can help women navigate this transition with confidence. If symptoms interfere with daily life, seek advice from a healthcare provider.
For compassionate care and expert guidance during menopause, trust the specialists at Ova Fertility and Women Care.



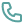



 No need to worry, your data is 100% Safe with us!
No need to worry, your data is 100% Safe with us!