Laparoscopic surgery, often referred to as minimally invasive surgery, is a technique that allows doctors to perform operations through small incisions rather than large cuts. This method has gained popularity in recent years due to its precision and effectiveness. It is widely used in various medical fields, including general surgery, gynecology, urology, and more.
How Laparoscopic Surgery Works
The procedure involves the use of a specialized instrument called a laparoscope. A laparoscope is a long, thin tube equipped with a high-resolution camera and a light source. During the surgery, the laparoscope is inserted into the body through a small incision. The camera transmits images to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see the area being operated on in real-time.
In addition to the laparoscope, other small instruments are inserted through separate incisions to perform the actual operation. The surgeon manipulates these instruments while viewing the magnified images on the monitor.
The Steps Involved in Laparoscopic Surgery
- Preparation: Before the procedure, the patient is typically placed under general anesthesia to ensure comfort and immobility during the operation.
- Creating Access: A small incision is made near the surgical site, and a trocar (a hollow tube) is inserted. The laparoscope is passed through this tube to provide visual access to the internal organs.
- Inflating the Area: To improve visibility, the surgeon introduces carbon dioxide gas into the abdominal cavity. This creates space by lifting the abdominal wall away from the organs.
- Performing the Surgery: Additional instruments are inserted through other small incisions. The surgeon uses these tools to perform the required operation, such as removing a diseased organ or repairing tissue.
- Closing the Incisions: Once the surgery is complete, the instruments and gas are removed. The incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
Common Applications of Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is used to treat a wide range of medical conditions. Some common applications include:
- Appendectomy: Removal of an inflamed appendix.
- Cholecystectomy: Removal of the gallbladder due to gallstones or other issues.
- Hernia Repair: Correction of hernias in the abdominal wall.
- Gynecological Procedures: Treatments for conditions such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, and fibroids.
- Bariatric Surgery: Procedures like gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy to aid in weight loss.
- Diagnostic Procedures: Examining internal organs to diagnose conditions or identify the cause of unexplained symptoms.
The Role of Technology in Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery relies heavily on advanced technology. High-definition cameras and specialized instruments allow surgeons to perform complex procedures with precision. Some surgeries even use robotic-assisted systems, where the surgeon controls robotic arms to enhance accuracy and dexterity.
Advantages for Surgeons
For surgeons, laparoscopic techniques provide enhanced visibility of the surgical field. The camera’s magnification offers a detailed view, enabling precise movements and reducing the likelihood of unintended damage to surrounding tissues. The instruments used are designed for fine manipulation, allowing intricate procedures to be performed effectively.
Patient Experience and Recovery
The smaller incisions used in laparoscopic surgery often result in less disruption to surrounding tissues. This technique is frequently used when traditional open surgery might require larger incisions and extended hospital stays. Many patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery experience shorter recovery periods and less visible scarring, but the exact outcomes can vary based on the type of surgery and individual factors.
Preparing for Laparoscopic Surgery
Before undergoing laparoscopic surgery, patients typically have a pre-operative consultation with their doctor. This includes:
- A review of medical history.
- A discussion of the procedure and what to expect.
- Instructions regarding fasting or medications.
Pre-operative tests, such as blood work or imaging studies, may also be conducted to ensure the patient is ready for the procedure.
Innovations in Laparoscopic Surgery
The field of laparoscopic surgery continues to evolve. Innovations such as 3D imaging, single-port laparoscopic surgery, and enhanced surgical tools are improving the precision and efficiency of these procedures. Researchers are also exploring ways to expand the use of laparoscopic techniques to more complex surgeries, offering new possibilities in the medical field.
Post-Surgery Care and Follow-Up
After laparoscopic surgery, patients are usually monitored in a recovery room before being discharged. Most individuals can return to normal activities relatively quickly, but doctors often provide specific guidelines regarding rest, diet, and activity levels. Follow-up visits are essential to ensure proper healing and to address any concerns or questions.
Future of Laparoscopic Surgery
As technology continues to advance, laparoscopic surgery is expected to become even more sophisticated. Emerging techniques and tools may allow surgeons to perform highly complex procedures with greater precision. This progress holds the potential to further transform the way surgeries are conducted.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic surgery represents a significant advancement in modern medicine. By using small incisions and specialized tools, this technique enables surgeons to perform a wide variety of procedures effectively. Whether for diagnostic purposes or treatment, laparoscopic surgery continues to play a vital role in improving patient outcomes and expanding the possibilities of surgical care.



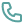



 No need to worry, your data is 100% Safe with us!
No need to worry, your data is 100% Safe with us!